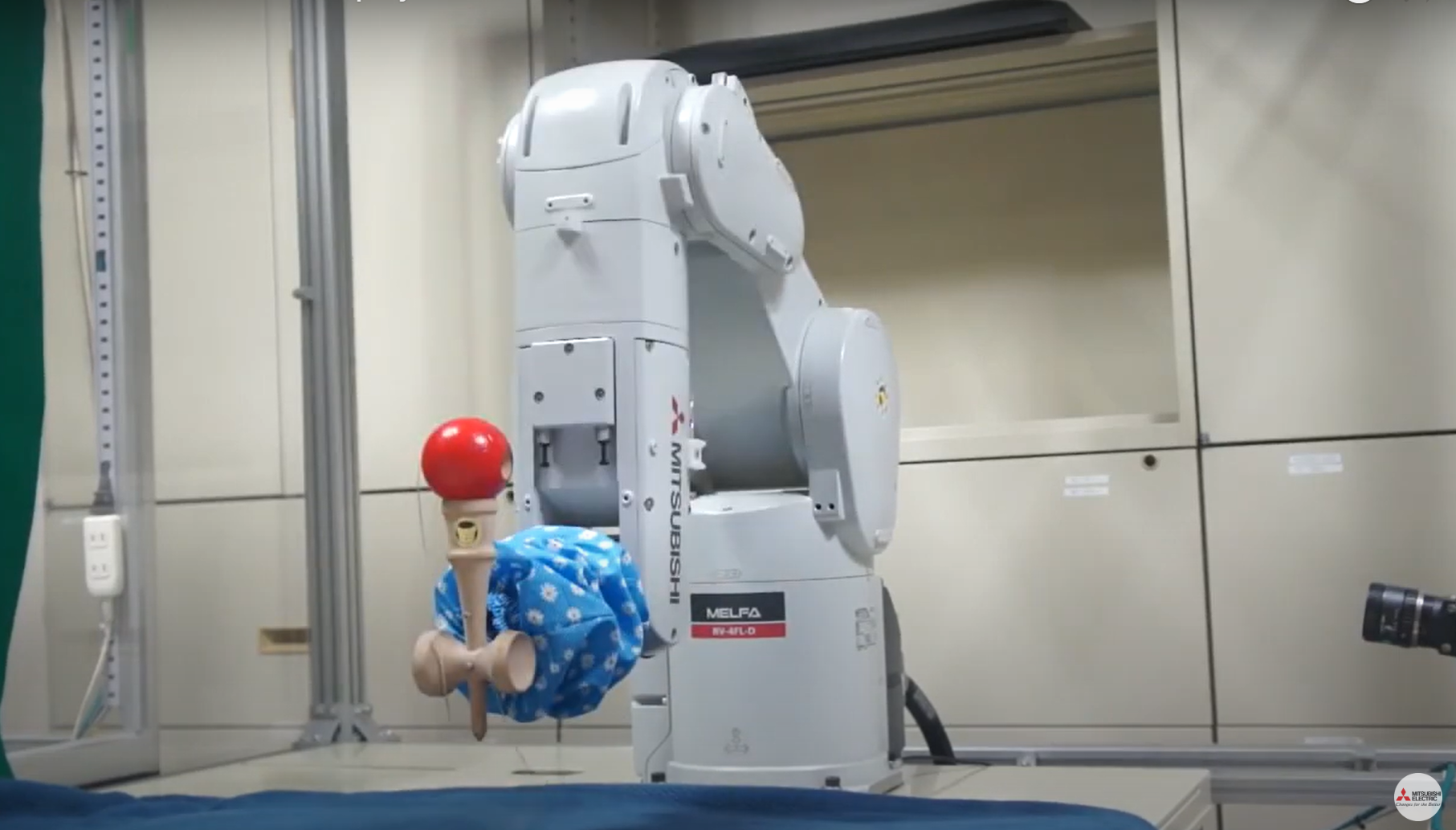
The Smooth Coordination Between Intelligent AI Robot and Traditional Japanese Game "Kendama"
With techniques requiring precision and dexterity, does this game pose a challenge for Mitsubishi Electric's intelligent AI robot?
Kendama is a traditional Japanese game made of wood. This game consists of a stick called Ken and a ball with a hole, called Dama, both connected by a string.
Thân Ken có 4 vị trí để hứng bóng là hai vị trí đối xứng, phần đáy và phần đầu nhọn. Người chơi sẽ tung quả bóng lên để bóng rơi vào vị trí hứng hoặc đầu nhọn. Thoạt nhìn, cách chơi có vẻ khá đơn giản. Tuy nhiên, để có thể làm chủ được nó, bạn phải cần đến rất nhiều kỹ thuật khác nhau như cân bằng bóng, tính toán lực tung… để đưa được bóng vào đúng vị trí.
The Ken stick has 4 positions to catch the ball: two symmetrical positions, the bottom, and the sharp end. Players will toss the ball up to make it fall into the catching position or the sharp end. At first glance, the gameplay seems quite simple. However, to master it, you need many different techniques such as balancing the ball, calculating the throwing force, etc., to get the ball into the right position.